Die Messmethoden zur Selbstentladung von Lithium-Ionen-Batterien werden hauptsächlich in zwei Kategorien unterteilt: 1) statische Messmethode, bei der die Selbstentladungsrate durch längeres Stehenlassen der Batterie ermittelt wird; 2) Dynamische Messmethode zur Realisierung der Parameteridentifizierung der Batterie im dynamischen Prozess.
Statische Messmethode
At present, the mainstream self-discharge measurement method of lithium-ion batteries is to static the battery for a long time under certain environmental conditions, and measure the change of battery parameters before and after static to characterize the self-discharge degree of lithium-ion batteries. According to the different measurement parameters, static measurement is mainly divided into three categories: capacity measurement, open circuit voltage measurement, and current measurement.
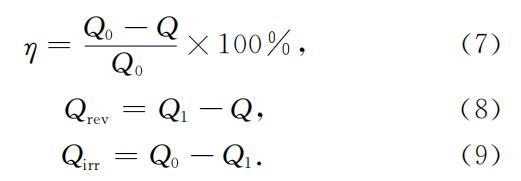
1. Capacity measurement
Before the battery is allowed to stand for a long time, charge and discharge the battery once and record the discharge capacity Q0 before standing. After standing, the battery is discharged in the same way, and the discharge capacity Q after standing is recorded.
According to equation (7), the self-discharge rate η of the battery can be calculated. Then the battery is charged and discharged in the same way, and the battery discharge capacity Q1 after the cycle is recorded. According to equations (8) and (9), the reversible self-discharge Qrev and irreversible self-discharge Qirr of the battery can be calculated respectively. A diagram of the method is shown in Figure 1.
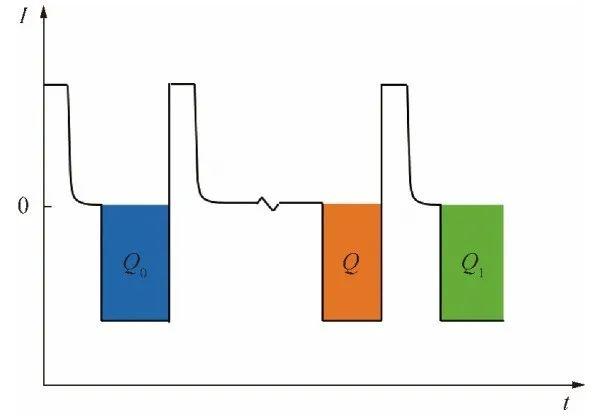
FIG. 1 Schematic diagram of capacity measurement method
In the battery testing manual issued by the international standardization bodies and relevant government departments and industry associations, the relevant provisions are made for the detection of battery self-discharge through capacity measurement: The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) issued "Batteries and battery packs containing alkaline or other non-acidic electrolytes: Portable secondary lithium Batteries and accumulators "(IEC 61960) stipulates that the battery will be in the state of 50%SOC, stored at the ambient temperature of (20±5)℃ for 90 days, and the discharge of the battery after recharging should not be less than 85% of the rated capacity, the specific measurement process is shown in Figure 2a. The battery test manual for electric vehicles issued by the United States Automotive Research Council (USCAR) stipulates that the actual power level corresponding to the operating range of the battery should be measured before measurement. After the battery is discharged at a C/3 ratio of 50% of the available electricity, it is stored at an ambient temperature of 30 ° C for 30 days, and the discharge of the battery is measured after recharging. The "Performance Requirements and Test Methods of power batteries for Electric Vehicles" (GB/T 31486) issued by the Standardization Administration of China is similar to the IEC standard, which stipulates the measurement test process of charge retention and capacity recovery ability. Taking the room temperature test as an example, the battery is stored for 8d at room temperature, the charge retention rate is not less than 85% of the initial capacity, and the capacity recovery is not less than 90% of the initial capacity. The specific measurement process is shown in Figure 2b.

FIG. 2 Measurement procedure (a) specified in IEC 61960 and measurement procedure (b) specified in GB/T 31486
2. Open circuit voltage measurement
The self-discharge degree of lithium-ion battery is characterized by measuring the change of the open-circuit voltage during the battery resting process. The advantage of this method is that it is simpler and less time-consuming than measuring capacity. The disadvantage is that for lithium-ion batteries with a long voltage platform on the open volt-soc curve (such as LFP batteries), the battery voltage changes little in a large SOC range, and it is difficult to characterize the degree of self-discharge by measuring the open voltage, that is, the method has a certain range of application.
3. Current measurement
The lithium-ion battery is charged by micro-current to keep the battery voltage unchanged, and the charging current value when stable is self-discharge current [1-2]. This small current may not be stabilized for several months, and the stability time of different battery designs is different, and the generally recommended measurement time is at least one week [3].
This method has similar problems to the method of measuring open circuit voltage, that is, for lithium-ion batteries with long voltage platforms, the effectiveness of this method is challenged. In addition, because the self-discharge current of lithium-ion batteries is extremely small, generally C/50000 or lower, to apply and measure this tiny order of current, the requirements for experimental instruments are high.
The above conventional static current measurement method is improved to some extent. An electrochemical workstation is used to apply a constant voltage lower than the open current to the battery, and the current flowing through the circuit is measured at the same time. The current-time curve of the battery without self-discharge and the battery with self-discharge is shown in Figure 3a.
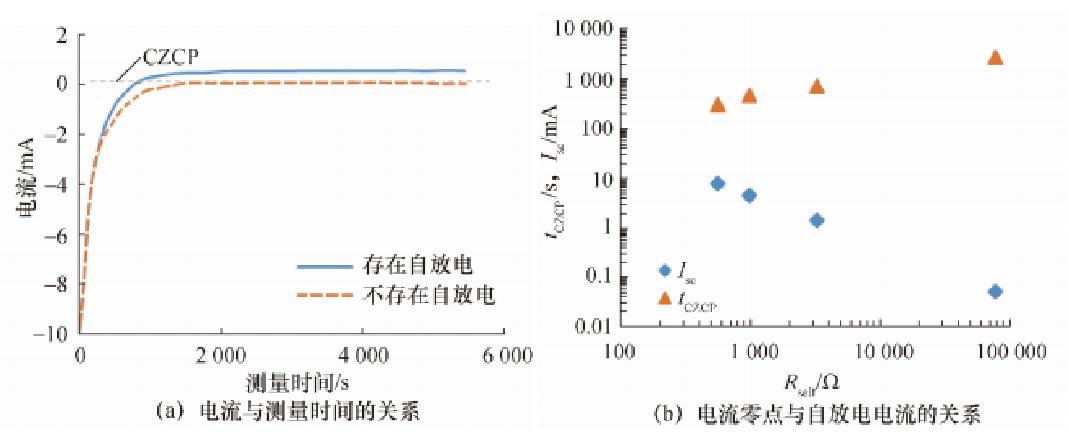
FIG. 3 Partial experimental results of Sazhin current measurement method
By actively applying a constant voltage, controlling the battery to reach the equilibrium state, and, measuring the current flowing through the circuit during this process, the measurement time can be shortened. In addition, the crossing point (CZCP) where the current is zero can also be used as a parameter to characterize the self-discharge rate. As shown in Figure 3b, the logarithm of tCZCP when the current Isc reaches zero is positively correlated with the logarithm of the self-discharge resistance Rself.
However, this method also has a serious disadvantage, that is, the accuracy of the experimental equipment is high. The electrochemical workstation used in the experiment has a voltage resolution of 100uV(14.5V range) and a current resolution of 1pA(200nA range).
Taken together, the above three methods are very time-consuming, with the experimental period ranging from one day to tens of days, and the reduction of the measurement time in the current measurement scenario requires high equipment costs.
Dynamic measurement method
Dynamic measurement method, that is, to realize the parameter identification of the battery in the dynamic process. To shorten the measurement time, save space resources and human resources. One method is to speed up the self-discharge rate by changing conditions such as the ambient temperature and SOC of the battery, so that the measurement parameters can change relatively large in a short period. Although this method saves the experiment time, it also speeds up the aging of the battery and increases the damage to the battery, which is only suitable for laboratory research and is not suitable for large-scale applications in actual production. Another method is to introduce self-discharge resistance based on the existing mature lithium-ion battery equivalent circuit model, and measure the self-discharge rate of lithium-ion batteries in the dynamic process through different parameter identification means.
Based on the automatic system identification theory, the lithium-ion battery is simplified into a first-order resistance-capacitance (R-C) equivalent circuit, and the same charge and discharge current is applied to the lithium-ion battery and the equivalent circuit, and the parameters of the equivalent circuit are adjusted according to the difference in output voltage until the difference between the two approaches zero, and the self-discharge resistance value of the lithium-ion battery is obtained. The total measurement time required for this method is about 12h. However, this method equates the battery to a passive circuit and does not consider the influence of the change of the battery's state of charge on the output voltage during the experiment.
Reduce the battery to an equivalent circuit as shown in Figure 4. Where: Rp, i is the electrochemical reaction resistance, Cp, i is the double electric layer capacitor, Rself is the self-discharge resistance, and C is the battery equivalent capacitance. Applying a short-time current pulse to the lithium-ion battery measures the voltage change during the subsequent resting process, and the self-discharge resistance value is further analyzed. This method only considers the reaction that plays a leading role in each stage of the static process and decouples the complex reactants, reducing the calculation and shortening the measurement time.
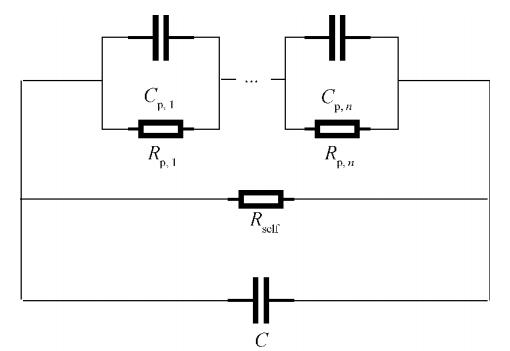
Figure 4 Lithium-ion battery equivalent circuit
Specifically, the recovery of overvoltage plays a leading role in the initial stage of static, and the self-discharge of the battery at the end of static plays a leading role. The time constant of self-discharge can be analyzed by the data at the end of the static period, and then the voltage drop caused by self-discharge in the recovery period of overvoltage can be compensated, and the equivalent capacitance of the battery can be solved, and the self-discharge resistance value can be obtained. This method can obtain the self-discharge resistance of lithium-ion batteries within 10 ~ 48h, saving a lot of time compared with the traditional method, but it still needs to consume a lot of static time to observe the stage where self-discharge plays a dominant role.
Die Auswirkung eines Kurzschlusses in der Batterie wird in zwei Kategorien unterteilt: Parametereffekt und Verbrauchseffekt. Darunter: Der Parametereffekt bedeutet, dass aufgrund des Vorhandenseins eines Kurzschlusswiderstands die gemessene Leerlaufspannung und der Innenwiderstand eine gewisse Abweichung vom tatsächlichen Wert aufweisen; Der Verbrauchseffekt bedeutet, dass aufgrund des Vorhandenseins eines Kurzschlusswiderstands die in der Batterie gespeicherte Energie kontinuierlich verbraucht wird und der Batterie-SOC weiter abnimmt, was zu einer gewissen Abweichung vom wahren Wert der Batterie-Leerlaufspannung führt Innenwiderstand vom Normalwert.

Im in den Formeln (10) und (11) dargestellten Batteriedifferenzmodell ist Ei die Leerlaufspannung der Batterie, Ri der Innenwiderstand der Batterie und Ui und I die gemessene Batteriespannung bzw. der gemessene Batteriestrom. Die Werte von ΔEi und ΔRi werden durch die rekursive Methode der kleinsten Quadrate ermittelt und die abnormalen Parameter, die den Schwellenwert überschreiten, werden durch eine statistische Methode identifiziert, um festzustellen, ob die Batterie einen internen Kurzschluss aufweist. Wenn der Kurzschlusswiderstand 100 Ω beträgt, kann die Methode die Identifizierung des internen Kurzschlusses frühestens in 4 Stunden und 43 Minuten realisieren.
Die oben genannten drei dynamischen Messmethoden vereinfachen die Lithium-Ionen-Batterie durch die Einführung von Ersatzschaltkreisen und anderen Mitteln und übernehmen innovative experimentelle Methoden zur Analyse des Selbstentladungswiderstandswerts, wodurch große Fortschritte bei der Verkürzung der Messzeit erzielt wurden.
Zusammenfassen
Die Methoden zur Messung der Selbstentladungsrate von Lithium-Ionen-Batterien durch statische Messung und dynamische Messung werden besprochen. Die wichtigsten Schlussfolgerungen lauten wie folgt:
1, die Nebenreaktion, die an der negativen Elektrode/Elektrolyt- und der positiven Elektrode/Elektrolyt-Grenzfläche auftritt, ist die Hauptquelle der Selbstentladung der Lithium-Ionen-Batterie und kann durch die Oberfläche der positiven Elektrode und die Zugabe von Zusatzstoffen in der negativen Elektrode verändert werden , Elektrolyt und andere Mittel, um das Auftreten einer Selbstentladung zu verhindern.
2. Im Batteriespeicherprozess sollte versucht werden, einen zu hohen oder zu niedrigen SOC-Zustand zu vermeiden, und die Umgebungstemperatur und Luftfeuchtigkeit sollten in einem relativ niedrigen Bereich gehalten werden.
3. Die derzeit gängige Selbstentladungsmessmethode ist eine statische Messung, die auf einem statischen Langzeitexperiment basiert. Das größte Problem bei dieser Methode besteht darin, dass die Messzeit zu lang ist, was zu einer enormen Verschwendung von Platz und Personalressourcen führt. Es wurden einige dynamische Messmethoden zur Parameteridentifizierung in Kombination mit Ersatzschaltkreismodellen vorgeschlagen, und es wurden einige Fortschritte bei der Verkürzung der Messzeit erzielt. Durch innovatives experimentelles Design ist die entkoppelte Identifizierung der Selbstentladung im dynamischen Prozess der Schlüsselpfad und die Entwicklungsrichtung für die Realisierung einer schnellen Selbstentladungsmessung in der Zukunft.
Kategorien
jüngste Beiträge
Scannen Sie den Scan zu WeChat:everexceed
